At 28 C, raw milk sours in 4.0 h but takes 48 h to sour in a refrigerator at 5 C. Estimate the activation energy in kJ>mol for the reaction that leads to the souring of milk.

The following mechanism has been proposed for the reaction of NO with H2 to form N2O and H2O:
NO(g) + NO(g) → N2O2(g)
N2O2(g) + H2(g) → N2O(g) + H2O(g)
(d) The observed rate law is rate = k[NO]2[H2]. If the proposed mechanism is correct, what can we conclude about the relative speeds of the first and second reactions?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Reaction Mechanism
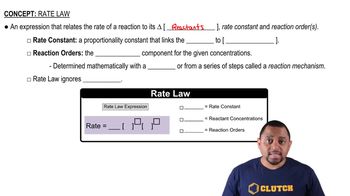
Rate Law
Rate-Determining Step

The following mechanism has been proposed for the reaction of NO with H2 to form N2O and H2O:
NO(g) + NO(g) → N2O2(g)
N2O2(g) + H2(g) → N2O(g) + H2O(g)
(a) Show that the elementary reactions of the proposed mechanism add to provide a balanced equation for the reaction.
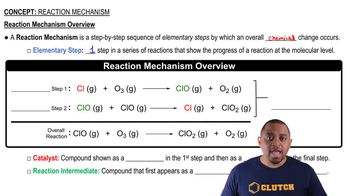
Ozone in the upper atmosphere can be destroyed by the following two-step mechanism:
Cl(g) + O3(g) → ClO(g) + O2(g)
ClO(g) + O(g) → Cl(g) + O2(g)
(a) What is the overall equation for this process?
Ozone in the upper atmosphere can be destroyed by the following two-step mechanism:
Cl(g) + O3(g) → ClO(g) + O2(g)
ClO(g) + O(g) → Cl(g) + O2(g)
(b) What is the catalyst in the reaction?
The gas-phase decomposition of ozone is thought to occur by the following two-step mechanism.
Step 1: O3(g) ⇌ O2(g) + O(g) (fast)
Step 2: O(g) + O3(g) → 2 O2 (slow)
(a) Write the balanced equation for the overall reaction.
