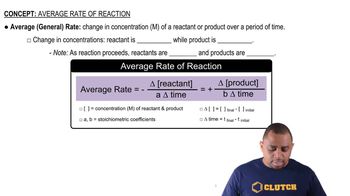
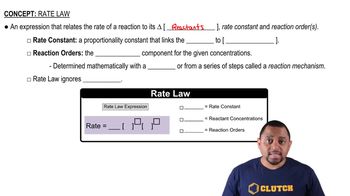
The following data were measured for the reaction BF3(g) + NH3(g) → F3BNH3(g):
Experiment [BF3] (M) [NH3] (M) Initial Rate (M/s)
1 0.250 0.250 0.2130
2 0.250 0.125 0.1065
3 0.200 0.100 0.0682
4 0.350 0.100 0.1193
5 0.175 0.100 0.0596
(b) What is the overall order of the reaction?