From the following data for the first-order gas-phase isomerization of CH3NC at 215 C, calculate the firstorder rate constant and half-life for the reaction: Time (s) Pressure CH3nC (torr) 0 502 2000 335 5000 180 8000 95.5 12,000 41.7 15,000 22.4

Consider the data presented in Exercise 14.19. (c) What is the half-life for the reaction?

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Half-life

Reaction Rate
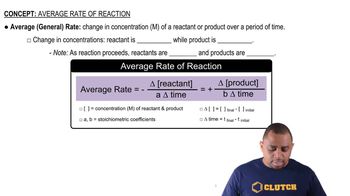
Integrated Rate Laws
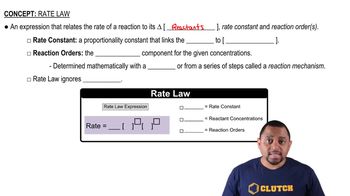
Consider the data presented in Exercise 14.19. (a) By using appropriate graphs, determine whether the reaction is first order or second order.
The gas-phase decomposition of NO2, 2 NO2(g) → 2 NO(g) + O2(g), is studied at 383°C, giving the following data:
Time (s) [NO2] (M)
0.0 0.100
5.0 0.017
10.0 0.0090
15.0 0.0062
20.0 0.0047
(a) Is the reaction first order or second order with respect to the concentration of NO2?
(c) Predict the reaction rates at the beginning of the reaction for initial concentrations of 0.200 M, 0.100 M, and 0.050 M NO2.
Sucrose 1C12H22O112, commonly known as table sugar, reacts in dilute acid solutions to form two simpler sugars, glucose and fructose, both of which have the formula C6H12O6. At 23 C and in 0.5 M HCl, the following data were obtained for the disappearance of sucrose: Time (min) 3C12H22o11 4 1M2 0 0.316 39 0.274 80 0.238 140 0.190 210 0.146 (a) Is the reaction first order or second order with respect to 3C12H22O114?
