Textbook Question
What is the molecularity of each of the following elementary reactions? Write the rate law for each. (a) Cl2(g) → 2 Cl(g)

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance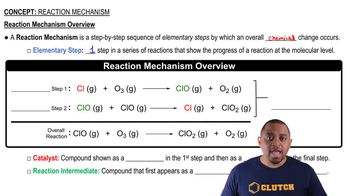


What is the molecularity of each of the following elementary reactions? Write the rate law for each. (a) Cl2(g) → 2 Cl(g)
The temperature dependence of the rate constant for a reaction is tabulated as follows: Temperature (K) k 1M 1 s1 2 600 0.028 650 0.22 700 1.3 750 6.0 800 23 Calculate Ea and A.
(b) What is the difference between a unimolecular and a bimolecular elementary reaction?