(b) The reaction 2 NO1g2 + Cl21g2¡2 NOCl1g2 is carried out in a closed vessel. If the partial pressure of NO is decreasing at the rate of 56 torr/min, what is the rate of change of the total pressure of the vessel?

A reaction A + B → C obeys the following rate law: Rate = k[B]2. (b) What are the reaction orders for A and B? What is the overall reaction order?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Rate Law
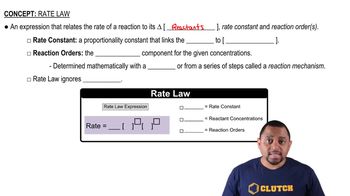
Reaction Order

Overall Reaction Order

A reaction A + B → C obeys the following rate law: Rate = k[B]2. (a) If [A] is doubled, how will the rate change? Will the rate constant change?
A reaction A + B → C obeys the following rate law: Rate = k[B]2. (c) What are the units of the rate constant?
Consider a hypothetical reaction between A, B, and C that is first order in A, zero order in B, and second order in C. (a) Write the rate law for the reaction.
Consider a hypothetical reaction between A, B, and C that is first order in A, zero order in B, and second order in C. (b) How does the rate change when [A] is doubled and the other reactant concentrations are held constant? (c) How does the rate change when [B] is tripled and the other reactant concentrations are held constant? (d) How does the rate change when [C] is tripled and the other reactant concentrations are held constant? (f) By what factor does the rate change when the concentrations of all three reactants are cut in half?
