Textbook Question
Which of the following in each pair is likely to be more soluble in water: (c) HCl or ethyl chloride (CH3CH2Cl)? Explain in each case.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

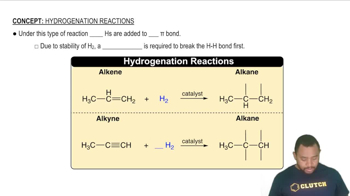

Which of the following in each pair is likely to be more soluble in water: (c) HCl or ethyl chloride (CH3CH2Cl)? Explain in each case.
Indicate whether each statement is true or false: (c) As you cool a saturated solution from high temperature to low temperature, solids start to crystallize out of solution if you achieve a supersaturated solution.
Indicate whether each statement is true or false: (d) If you take a saturated solution and raise its temperature, you can (usually) add more solute and make the solution even more concentrated.
(a) Calculate the mass percentage of Na2SO4 in a solution containing 10.6 g of Na2SO4 in 483 g of water.