Textbook Question
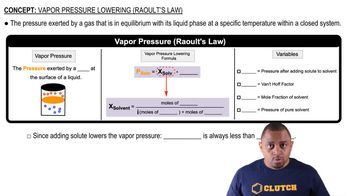
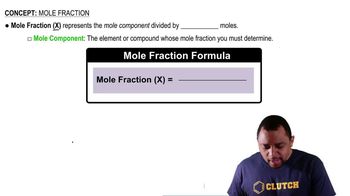
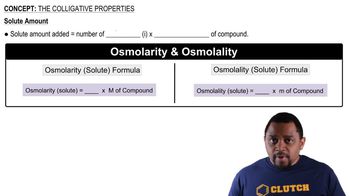
The vapor pressure of pure water at 60 °C is 149 torr. The vapor pressure of water over a solution at 60 °C containing equal numbers of moles of water and ethylene glycol (a nonvolatile solute) is 67 torr. Is the solution ideal according to Raoult's law?