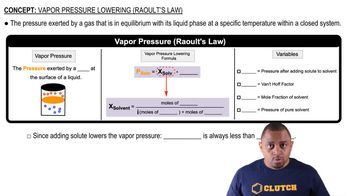
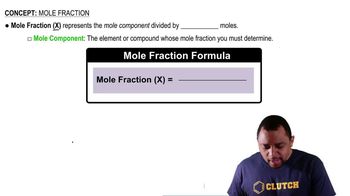
Textbook Question
At 63.5 °C, the vapor pressure of H2O is 175 torr, and that of ethanol (C2H5OH) is 400 torr. A solution is made by mixing equal masses of H2O and C2H5OH. (b) Assuming ideal solution behavior, what is the vapor pressure of the solution at 63.5 °C?