Ascorbic acid (vitamin C, C6H8O6) is a water-soluble vitamin. A solution containing 80.5 g of ascorbic acid dissolved in 210 g of water has a density of 1.22 g/mL at 55 °C. Calculate (a) the mass percentage,
Ch.13 - Properties of Solutions

Brown14th EditionChemistry: The Central ScienceISBN: 9780134414232Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 13, Problem 48c
Ascorbic acid (vitamin C, C6H8O6) is a water-soluble vitamin. A solution containing 80.5 g of ascorbic acid dissolved in 210 g of water has a density of 1.22 g/mL at 55 °C. Calculate (c) the molality,
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the formula for molality: \( m = \frac{\text{moles of solute}}{\text{kilograms of solvent}} \).
Calculate the moles of ascorbic acid using its molar mass. The molar mass of C\(_6\)H\(_8\)O\(_6\) is calculated as follows: \( 6(12.01) + 8(1.01) + 6(16.00) \).
Convert the mass of the solvent (water) from grams to kilograms. Since the mass of water is 210 g, convert it to kilograms by dividing by 1000.
Use the moles of ascorbic acid and the kilograms of water to calculate the molality using the formula from step 1.
Ensure all units are consistent and check calculations for accuracy.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
3mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Molality
Molality is a measure of the concentration of a solute in a solution, defined as the number of moles of solute per kilogram of solvent. It is particularly useful in situations where temperature changes may affect the volume of the solution, as it is based on mass rather than volume. The formula for calculating molality (m) is m = moles of solute / mass of solvent (in kg).
Recommended video:
Guided course
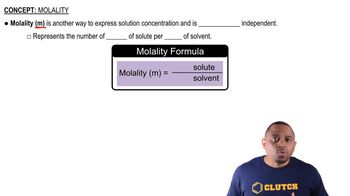
Molality
Moles of Solute
To calculate molality, one must first determine the number of moles of the solute, which in this case is ascorbic acid. The number of moles can be calculated using the formula: moles = mass (g) / molar mass (g/mol). The molar mass of ascorbic acid (C6H8O6) is approximately 176.12 g/mol, which is essential for converting grams of ascorbic acid into moles.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Mole Fraction Formula
Density and Volume Relationship
Density is defined as mass per unit volume (g/mL), and it plays a crucial role in determining the volume of the solvent when given its mass. In this problem, the density of the solution is provided, allowing us to calculate the volume of the water used. Understanding the relationship between mass, density, and volume is essential for accurately determining the mass of the solvent in kilograms for the molality calculation.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Relationship of Volume and Moles Example
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
Ascorbic acid (vitamin C, C6H8O6) is a water-soluble vitamin. A solution containing 80.5 g of ascorbic acid dissolved in 210 g of water has a density of 1.22 g/mL at 55 °C. Calculate (d) the molarity of ascorbic acid in this solution.
Textbook Question
The density of acetonitrile (CH3CN) is 0.786 g/mL and the density of methanol (CH3OH) is 0.791 g/mL. A solution is made by dissolving 22.5 mL of CH3OH in 98.7 mL of CH3CN. (a) What is the mole fraction of methanol in the solution?
Textbook Question
The density of acetonitrile (CH3CN) is 0.786 g/mL and the density of methanol (CH3OH) is 0.791 g/mL. A solution is made by dissolving 22.5 mL of CH3OH in 98.7 mL of CH3CN. (b) What is the molality of the solution?
