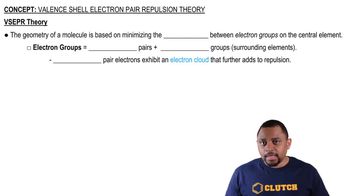
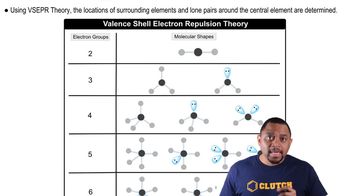
Textbook Question
At ordinary body temperature (37 °C), the solubility of N2 in water at ordinary atmospheric pressure (1.0 atm) is 0.015 g/L. Air is approximately 78 mol % N2. (b) At a depth of 100 ft in water, the external pressure is 4.0 atm. What is the solubility of N2 from air in blood at this pressure?