Indicate the type of solid (molecular, metallic, ionic, or covalent-network) for each compound: (c) Ta2O5 (melting point, 1872°C)
Ch.12 - Solids and Modern Materials

Brown14th EditionChemistry: The Central ScienceISBN: 9780134414232Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 12, Problem 18
You are given a white substance that melts at 100 °C. The substance is soluble in water. Neither the solid nor the solution is a conductor of electricity. Which type of solid (molecular, metallic, covalent-network, or ionic) might this substance be?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: Consider the melting point of the substance. A melting point of 100 °C suggests that the substance is not a metallic or covalent-network solid, as these typically have much higher melting points.
Step 2: Evaluate the solubility in water. The fact that the substance is soluble in water suggests it could be either ionic or molecular, as both types can dissolve in water under certain conditions.
Step 3: Analyze the electrical conductivity. Neither the solid nor the solution conducts electricity, which rules out ionic solids, as they typically conduct electricity when dissolved in water due to the presence of free ions.
Step 4: Consider the properties of molecular solids. Molecular solids often have low melting points, are soluble in water, and do not conduct electricity, which matches the properties of the given substance.
Step 5: Conclude that the substance is most likely a molecular solid, based on its melting point, solubility, and lack of electrical conductivity.
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Melting Point
The melting point is the temperature at which a solid becomes a liquid. It is a critical property that helps classify substances. For example, ionic compounds typically have high melting points due to strong electrostatic forces, while molecular solids often have lower melting points. In this case, the substance melts at 100 °C, suggesting it may not be ionic.
Recommended video:
Guided course
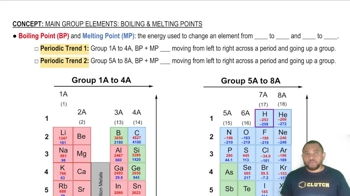
Boiling Point and Melting Point
Solubility in Water
Solubility refers to the ability of a substance to dissolve in a solvent, such as water. Substances that are soluble in water can interact favorably with water molecules. Ionic compounds and some polar molecular compounds tend to be soluble, while nonpolar substances are generally not. The solubility of the given substance indicates it may be a molecular solid.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Solubility and Insolubility
Electrical Conductivity
Electrical conductivity is the ability of a substance to conduct electricity, which depends on the presence of charged particles. Ionic solids conduct electricity when dissolved in water or melted, as they dissociate into ions. In contrast, molecular solids do not conduct electricity in any state, which aligns with the observation that neither the solid nor the solution conducts electricity, suggesting the substance is likely molecular.
Recommended video:
Guided course
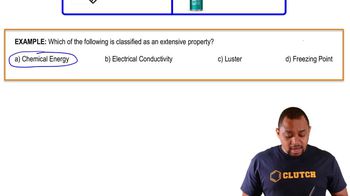
Extensive Property Example
Related Practice
Textbook Question
2
views
Textbook Question
You are given a gray substance that melts at 700 °C; the solid is a conductor of electricity and is insoluble in water. Which type of solid (molecular, metallic, covalent-network, or ionic) might this substance be?
Textbook Question
(a) Draw a picture that represents a crystalline solid at the atomic level.
Textbook Question
(b) Now draw a picture that represents an amorphous solid at the atomic level.
Textbook Question
Two patterns of packing for two different circles of the same size are shown here. For each structure (b) determine the angle between the lattice vectors, g, and determine whether the lattice vectors are of the same length or of different lengths; (i)
(ii)
