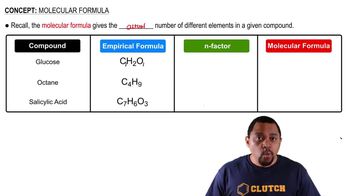
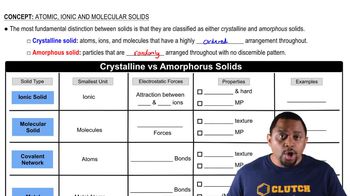
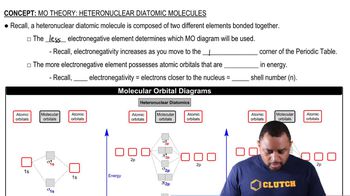
Polymers
Polymers are large molecules made up of repeating structural units called monomers, linked together by covalent bonds. Polyethylene, for example, is a polymer formed from the polymerization of ethylene monomers. In contrast, n-decane is a simple hydrocarbon with a fixed number of atoms and does not consist of repeating units, thus classifying it as a non-polymeric substance.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance