Textbook Question
What type of lattice—primitive cubic, body-centered cubic, or face-centered cubic—does each of the following structure types possess: (e) ZnS?


 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
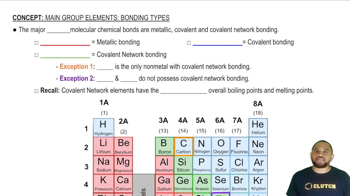


What type of lattice—primitive cubic, body-centered cubic, or face-centered cubic—does each of the following structure types possess: (e) ZnS?
Energy bands are considered continuous due to the large number of closely spaced energy levels. The range of energy levels in a crystal of copper is approximately 1 × 10–19 J. Assuming equal spacing between levels, the spacing between energy levels may be approximated by dividing the range of energies by the number of atoms in the crystal. (b) Determine the average spacing in J between energy levels in the copper metal in part (a).