Consider the sample of gas depicted here. What would the drawing look like if the volume and temperature remained constant while you removed enough of the gas to decrease the pressure by a factor of 2? (a) It would contain the same number of molecules. (b) It would contain half as many molecules. (c) It would contain twice as many molecules. (d) There is insufficient data to say.
Ch.10 - Gases

Brown14th EditionChemistry: The Central ScienceISBN: 9780134414232Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 10, Problem 2b
You have a sample of gas in a container with a movable piston, such as the one in the drawing. (b) Redraw the container to show what it might look like if the external pressure on the piston is increased from 101.3 kPa to 202.7 kPa while the temperature is kept constant.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the initial conditions of the gas: the initial pressure is 101.3 kPa, and the temperature is constant.
Recognize that the problem involves a change in external pressure on the gas, which affects the volume of the gas according to Boyle's Law.
Recall Boyle's Law: \( P_1V_1 = P_2V_2 \), where \( P \) is pressure and \( V \) is volume. Since the temperature is constant, this law applies.
Understand that increasing the external pressure from 101.3 kPa to 202.7 kPa will cause the volume of the gas to decrease, as pressure and volume are inversely related.
Redraw the container with the piston pushed further into the container, indicating a smaller volume of gas, while ensuring the piston is still movable and the temperature remains constant.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
1mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
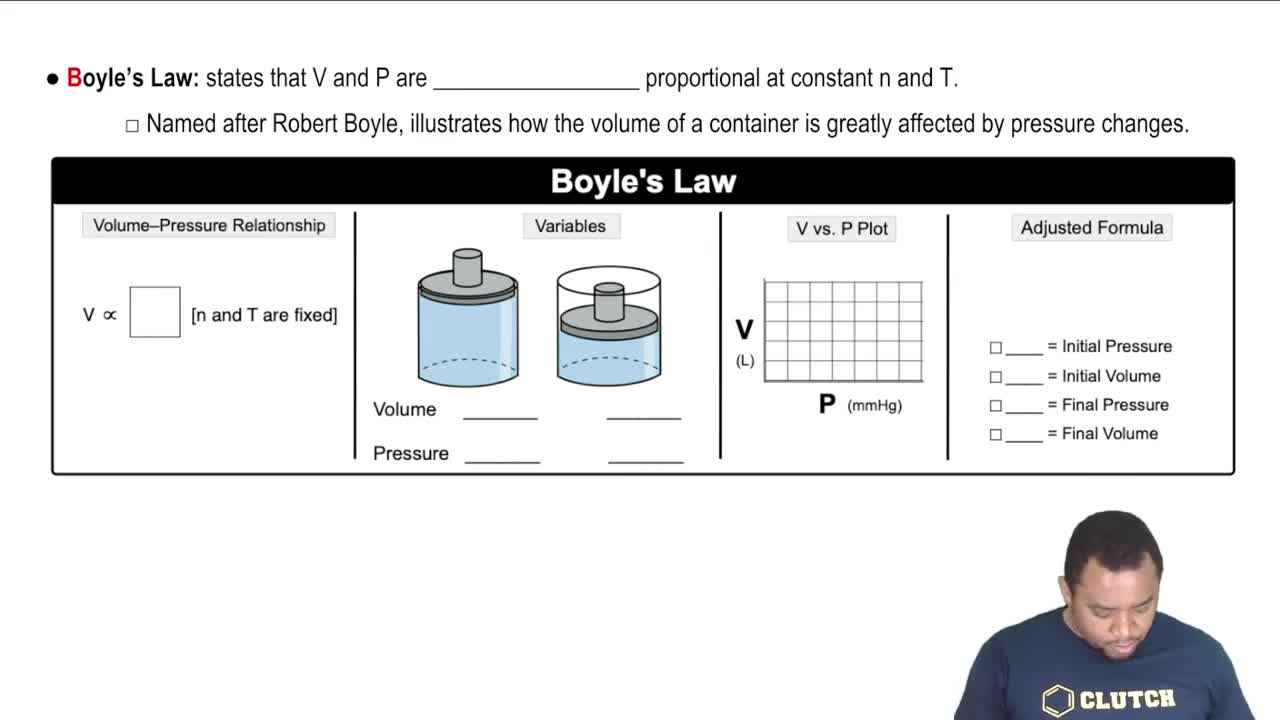
Boyle's Law
Boyle's Law states that the pressure of a gas is inversely proportional to its volume when the temperature is held constant. This means that if the pressure on a gas increases, its volume decreases, and vice versa. This relationship is crucial for understanding how changes in external pressure affect the behavior of gases in a closed system.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Boyle's Law
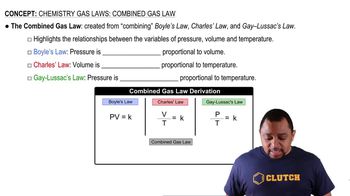
Gas Laws
Gas laws describe the behavior of gases under various conditions of pressure, volume, and temperature. They include Boyle's Law, Charles's Law, and Avogadro's Law, among others. Understanding these laws helps predict how a gas will respond to changes in its environment, such as the effect of increased external pressure on a gas contained in a piston.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Combined Gas Law
Piston Mechanism
A piston mechanism is a device that allows for the compression or expansion of gases by moving a piston within a cylinder. When external pressure is applied to the piston, it compresses the gas, reducing its volume. This concept is essential for visualizing how the gas sample will change in response to the increased pressure in the given scenario.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Reaction Mechanism Overview
Related Practice
Textbook Question
7
views
Textbook Question
Imagine that the reaction 2 CO1g2 + O21g2¡2 CO21g2 occurs in a container that has a piston that moves to maintain a constant pressure when the reaction occurs at constant temperature. Which of the following statements describes how the volume of the container changes due to the reaction: (a) the volume increases by 50%, (b) the volume increases by 33%, (c) the volume remains constant, (d) the volume decreases by 33%, (e) the volume decreases by 50%.
1
views
