Textbook Question
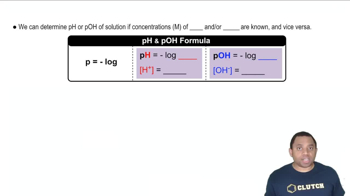
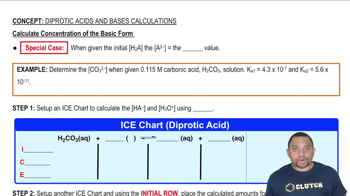
Addition of the indicator methyl orange to an unknown solution leads to a yellow color. The addition of bromthymol blue to the same solution also leads to a yellow color. (b) What is the range (in whole numbers) of possible pH values for the solution?