In qualitative analysis, Ca2+ and Ba2+ are seperated from Na+, K+, Mg2+ by adding aqueous (NH4)2CO3 to a solution that also contains aqueous NH3 (Figure 17.18). Assume that the concentrations after mixing are 0.080 M (NH4)2CO3 and 0.16 M NH3. (a) List all the Bronsted-Lowry acids and bases present initially, and identify the principal reaction.
Ch.17 - Applications of Aqueous Equilibria

Chapter 17, Problem 153b
A railroad tank car derails and spills 36 tons of concentrated sulfuric acid. The acid is 98.0 mass% H2SO4 and has a density of 1.836 g/mL. (b) How many kilograms of sodium carbonate are needed to completely neutralize the acid?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Determine the mass of pure \( \text{H}_2\text{SO}_4 \) in the spill by multiplying the total mass of the acid by the mass percentage of \( \text{H}_2\text{SO}_4 \) (98.0%).
Convert the mass of \( \text{H}_2\text{SO}_4 \) from tons to grams, knowing that 1 ton is equal to 907,185 grams.
Calculate the number of moles of \( \text{H}_2\text{SO}_4 \) using its molar mass (98.08 g/mol).
Write the balanced chemical equation for the neutralization reaction: \( \text{H}_2\text{SO}_4 + \text{Na}_2\text{CO}_3 \rightarrow \text{Na}_2\text{SO}_4 + \text{H}_2\text{O} + \text{CO}_2 \).
Use stoichiometry to determine the moles of \( \text{Na}_2\text{CO}_3 \) required, then convert this to mass in kilograms using the molar mass of \( \text{Na}_2\text{CO}_3 \) (105.99 g/mol).

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
5mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Neutralization Reaction
A neutralization reaction occurs when an acid reacts with a base to form water and a salt. In this case, sulfuric acid (H2SO4) will react with sodium carbonate (Na2CO3) to produce sodium sulfate (Na2SO4), water (H2O), and carbon dioxide (CO2). Understanding this reaction is crucial for determining the stoichiometry involved in neutralizing the acid.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Lewis Dot Structures: Neutral Compounds
Stoichiometry
Stoichiometry is the calculation of reactants and products in chemical reactions based on the balanced chemical equation. For the neutralization of sulfuric acid with sodium carbonate, the balanced equation helps to determine the molar ratios needed to find out how much sodium carbonate is required to neutralize a given amount of sulfuric acid.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Stoichiometry Concept
Concentration and Density
Concentration refers to the amount of solute in a given volume of solution, while density is the mass per unit volume of a substance. In this problem, the concentration of sulfuric acid is given in mass percent, and its density is provided, which allows for the conversion of mass to volume and vice versa, essential for calculating the amount of sodium carbonate needed for neutralization.
Recommended video:
Guided course
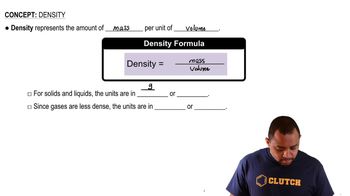
Density Concepts
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
A railroad tank car derails and spills 36 tons of concentrated sulfuric acid. The acid is 98.0 mass% H2SO4 and has a density of 1.836 g/mL. (a) What is the molarity of the acid?
Textbook Question
Some progressive hair coloring products marketed to men, such as Grecian Formula 16, contain lead acetate Pb(CH3CO2)2. As the coloring solution is rubbed on the hhair, the Pb2+ ions react with the sulfur atoms in hair proteins to give lead(II) sulfide (PbS), which is black. A typical coloring solution contains 0.3 mass% Pb(CH3CO2)2, and about 2 mL of the solution is used per application. (b) Suppose the hair is washed with shampoo and water that has pH = 5.50. How many washings would be required to remove 50% of the black color? Assume that 3 gal of water is used per washing and that the water becomes saturated with PbS. (c) Does the calculated number of washings look reason-able, given that frequent application of the coloring solution is recommended? What process(es) in addition to dissolution might contribute to the loss of color?
Textbook Question
Some progressive hair coloring products marketed to men, such as Grecian Formula 16, contain lead acetate Pb(CH3CO2)2. As the coloring solution is rubbed on the hair, the Pb2+ ions react with the sulfur atoms in hair proteins to give lead(II) sulfide (PbS), which is black. A typical coloring solution contains 0.3 mass% Pb(CH3CO2)2, and about 2 mL of the solution is used per application. (a) Assuming that 30% of the Pb(CH3CO2)2 is converted to PbS, how many milligrams of PbS are formed per application of the coloring solution?
Textbook Question
Neutralization reactions involving either a strong acid or a strong base go essentially to completion, and therefore we must take such neutralizations into account before calculating concentrations in mixtures of acids and bases. Consider a mixture of 3.28 g of Na3PO4 and 300.0 mL of 0.180 M HCl. Write balanced net ionic equations for the neutralization reactions and calculate the pH of the solution.
