Textbook Question
Calculate the pH of the solution that results from each mixture. a. 50.0 mL of 0.15 M HCHO2 with 75.0 mL of 0.13 M NaCHO2
1
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


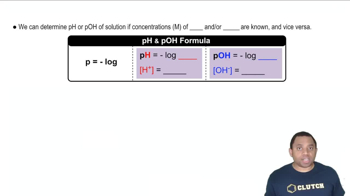
Calculate the pH of the solution that results from each mixture. a. 50.0 mL of 0.15 M HCHO2 with 75.0 mL of 0.13 M NaCHO2
Calculate the pH of the solution that results from each mixture. b. 125.0 mL of 0.10 M NH3 with 250.0 mL of 0.10 M NH4Cl
Calculate the ratio of NaF to HF required to create a buffer with pH = 3.90.
What mass of sodium benzoate should you add to 150.0 mL of a 0.15 M benzoic acid solution to obtain a buffer with a pH of 4.25? (Assume no volume change.)