Textbook Question
Write the formula for each ionic compound. d. calcium fluoride
1
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


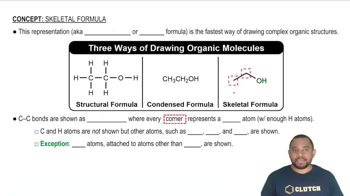
Write the formula for each ionic compound. d. calcium fluoride
Write the formula for each ionic compound. f. iron(II) phosphate
Write the name from the formula or the formula from the name for each hydrated ionic compound.
a. CoSO4•7 H2O
b. iridium(III) bromide tetrahydrate
c. Mg(BrO3)2•6 H2O
d. potassium carbonate dihydrate
Name each molecular compound. a. CO b. NI3 c. SiCl4 d. N4Se4
Name each molecular compound. a. SO3 c. BrF5
Name each molecular compound. b. SO2