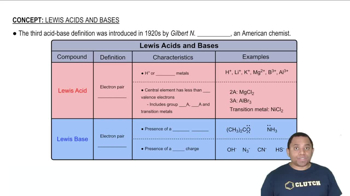
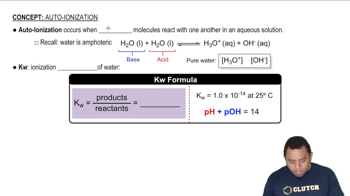
Textbook Question
What is the molar solubility of AgI in 0.20 M NaCN? (a) 6.2 x 10^-4 M(b) 1.0 x 10^-1 M(c) 7.6 x 10^-2 M(d) 2.1 x 10^-3 M


 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

The following pictures represent initial concentrations in solutions that contain a weak acid HA (pKa = 6.0) and its sodium salt NaA. (Na+ ions and solvent water molecules have been omitted for clarity.)
. (b) Draw a picture that represents the equilibrium state of solution (1) after the addition of two H3O+ ions.
The following pictures represent solutions that contain one or more of the compounds H2A, NaHA, and Na2A, where H2A is a weak diprotic acid. (Na+ ions and solvent water molecules have been omitted for clarity.)
(a) Which of the solutions are buffer solutions?