The reaction A¡products was monitored as a function of time. The results are shown here. Time (s) [A] (M) 0 1.000 25 0.914 50 0.829 75 0.744 100 0.659 125 0.573 150 0.488 175 0.403 200 0.318 Determine the order of the reaction and the value of the rate constant. What is the rate of reaction when [A] = 0.10 M?
Ch.15 - Chemical Kinetics

Chapter 15, Problem 60b
This reaction was monitored as a function of time: AB → A + B A plot of 1/[AB] versus time yields a straight line with a slope of +0.25/Ms. b. Write the rate law for the reaction.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the order of the reaction by analyzing the plot. A plot of 1/[AB] versus time that yields a straight line indicates a second-order reaction.
For a second-order reaction, the rate law is expressed as: rate = k[AB]^2.
The slope of the plot of 1/[AB] versus time is equal to the rate constant k for a second-order reaction.
Given that the slope is +0.25/Ms, this value represents the rate constant k.
Therefore, the rate law for the reaction is: rate = 0.25 [AB]^2.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
3mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Rate Law
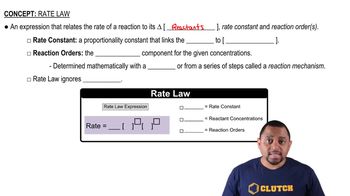
The rate law expresses the relationship between the rate of a chemical reaction and the concentration of its reactants. It is typically formulated as rate = k[A]^m[B]^n, where k is the rate constant, and m and n are the orders of the reaction with respect to each reactant. Understanding the rate law is essential for predicting how changes in concentration affect the reaction rate.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Rate Law Fundamentals
Order of Reaction
The order of a reaction refers to the power to which the concentration of a reactant is raised in the rate law. It indicates how the rate is affected by the concentration of that reactant. For example, if the order is 1, doubling the concentration will double the rate; if it is 2, doubling the concentration will quadruple the rate. The overall order is the sum of the individual orders.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Average Bond Order
Integrated Rate Laws
Integrated rate laws relate the concentration of reactants to time, allowing for the determination of reaction order from experimental data. For a second-order reaction, the integrated form is 1/[AB] = kt + 1/[AB]0, where [AB]0 is the initial concentration. The linear relationship observed in the plot of 1/[AB] versus time indicates that the reaction is second-order with respect to AB, which is crucial for writing the correct rate law.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Rate Law Fundamentals
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
This reaction was monitored as a function of time: A → B + C A plot of ln[A] versus time yields a straight line with slope -0.0105/s. a. What is the value of the rate constant (k) for this reaction at this temperature?
Textbook Question
Silver nitrate solutions are often used to plate silver onto other metals. What is the maximum amount of silver (in grams) that can be plated out of 4.8 L of an AgNO3 solution containing 3.4% Ag by mass? Assume that the density of the solution is 1.01 g/mL.
