A 25.0-mL sample of 0.050 M barium nitrate solution was mixed with 25.0 mL of 0.050 M sodium sulfate solution labeled with radioactive sulfur-35. The activity of the initial sodium sulfate solution was 1.22⨉106 Bq/mL. After the resultant precipitate was removed by filtration, the remaining filtrate was found to have an activity of 250 Bq/mL. (a) Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction that occurred.
Ch.21 - Nuclear Chemistry

Brown14th EditionChemistry: The Central ScienceISBN: 9780134414232Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 21, Problem 110
The two most common isotopes of uranium are 235U and238U. (d) 238U undergoes radioactive decay to 234Th. How manyprotons, electrons, and neutrons are gained or lost by the238U atom during this process?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the atomic number of uranium (U), which is 92. This means uranium has 92 protons and, in a neutral atom, 92 electrons.
Determine the number of neutrons in 238U by subtracting the atomic number from the mass number: 238 - 92 = 146 neutrons.
Understand that during the decay of 238U to 234Th, an alpha particle is emitted. An alpha particle consists of 2 protons and 2 neutrons.
Calculate the change in protons: 238U loses 2 protons, so the new element, thorium (Th), has 90 protons.
Calculate the change in neutrons: 238U loses 2 neutrons, so the new isotope, 234Th, has 144 neutrons. The number of electrons remains unchanged in this process.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
4mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Isotopes
Isotopes are variants of a chemical element that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. For example, uranium-235 (235U) and uranium-238 (238U) are isotopes of uranium, with 235U having 143 neutrons and 238U having 146 neutrons. This difference in neutron count affects their stability and radioactive properties.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Isotopes
Radioactive Decay
Radioactive decay is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by emitting radiation. This can result in the transformation of one element into another, as seen when 238U decays into 234Th. During this decay, particles such as alpha or beta particles may be emitted, leading to changes in the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus.
Recommended video:
Guided course
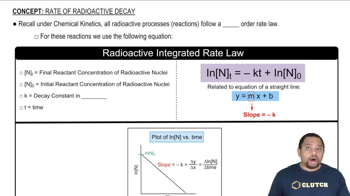
Rate of Radioactive Decay
Nuclear Reactions and Particle Changes
In nuclear reactions, the number of protons and neutrons in an atom can change, affecting its identity and charge. For instance, when 238U undergoes decay to form 234Th, it loses two protons and two neutrons, resulting in a new element. This change also affects the atom's overall charge, as the loss of protons alters the balance between protons and electrons.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Subatomic Particles
Related Practice
Textbook Question
3
views
Textbook Question
A 25.0-mL sample of 0.050 M barium nitrate solution was mixed with 25.0 mL of 0.050 M sodium sulfate solution labeled with radioactive sulfur-35. The activity of the initial sodium sulfate solution was 1.22 × 106 Bq/mL. After the resultant precipitate was removed by filtration, the remaining filtrate was found to have an activity of 250 Bq/mL. (b) Calculate the Ksp for the precipitate under the conditions of the experiment.
