Textbook Question
Calculate the ratio of CH3NH2 to CH3NH3Cl concentration required to create a buffer with pH = 10.24.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
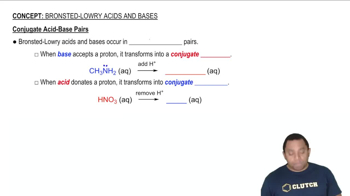

Calculate the ratio of CH3NH2 to CH3NH3Cl concentration required to create a buffer with pH = 10.24.
What mass of sodium benzoate should you add to 150.0 mL of a 0.15 M benzoic acid solution to obtain a buffer with a pH of 4.25? (Assume no volume change.)
A 100.0-mL buffer solution is 0.175 M in HClO and 0.150 M in NaClO. a. What is the initial pH of this solution?
A 100.0-mL buffer solution is 0.175 M in HClO and 0.150 M in NaClO. b. What is the pH after addition of 150.0 mg of HBr?