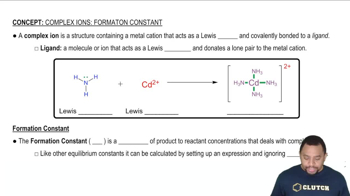
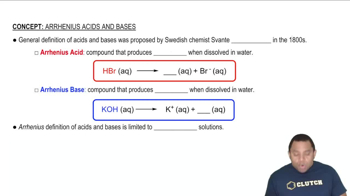
Textbook Question
Ammonium hydrogen sulfide, a stink bomb ingredient, decomposes to ammonia and hydrogen sulfide: Calculate the standard free-energy change for the rection at 25 °C if the total pressure resulting from the solid NH4S placed in an evacuated container is 0.658 atm at 25 °C.(a) -43.8 kJ(b) +1.04 kJ(c) -462 kJ(d) +5.51 kJ