To what volume should you dilute 50.0 mL of a 3.00 M KI solution so that 25.0 mL of the diluted solution contains 2.55 g of KI?
Ch.14 - Solutions

Chapter 14, Problem 58c
An aqueous KNO3 solution is made using 55.3 g of KNO3 diluted to a total solution volume of 2.00 L. Calculate the mass percent of the solution. (Assume a density of 1.05 g>mL for the solution.)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Calculate the mass of the solution using its volume and density: \( \text{mass of solution} = \text{density} \times \text{volume} \).
Convert the volume from liters to milliliters: \( 2.00 \text{ L} = 2000 \text{ mL} \).
Calculate the mass of the solution: \( \text{mass of solution} = 1.05 \text{ g/mL} \times 2000 \text{ mL} \).
Use the formula for mass percent: \( \text{mass percent} = \left( \frac{\text{mass of solute}}{\text{mass of solution}} \right) \times 100\% \).
Substitute the mass of KNO3 (55.3 g) and the calculated mass of the solution into the mass percent formula to find the mass percent.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
2mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Mass Percent
Mass percent is a way of expressing the concentration of a solute in a solution. It is calculated by taking the mass of the solute, dividing it by the total mass of the solution, and then multiplying by 100 to get a percentage. This concept is essential for understanding how much of a particular substance is present in a given amount of solution.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Mass Percent Calculation
Density
Density is defined as mass per unit volume and is a critical property of substances. In this context, the density of the solution (1.05 g/mL) allows us to convert the volume of the solution into mass, which is necessary for calculating the mass percent. Understanding density helps in determining how much the solute contributes to the overall mass of the solution.
Recommended video:
Guided course
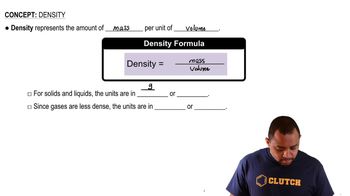
Density Concepts
Solution Preparation
Solution preparation involves dissolving a solute in a solvent to create a homogeneous mixture. In this case, KNO3 is the solute, and water is the solvent. Knowing how to prepare solutions and the relationship between mass, volume, and concentration is crucial for accurately calculating properties like mass percent in a solution.
Recommended video:
Guided course
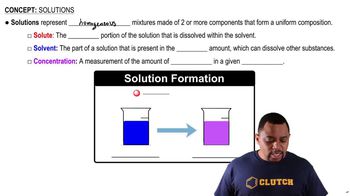
Solution Components
Related Practice
Textbook Question
1
views
Textbook Question
An aqueous NaCl solution is made using 102 g of NaCl diluted to a total solution volume of 1.00 L. Calculate the mass percent of the solution. (Assume a density of 1.08 g>mL for the solution.)
Textbook Question
An aqueous KNO3 solution is made using 55.3 g of KNO3 diluted to a total solution volume of 2.00 L. Calculate the molarity of the solution. (Assume a density of 1.05 g>mL for the solution.)
Textbook Question
An aqueous KNO3 solution is made using 55.3 g of KNO3 diluted to a total solution volume of 2.00 L. Calculate the molality of the solution. (Assume a density of 1.05 g>mL for the solution.)
Textbook Question
A dioxin-contaminated water source contains 0.085% dioxin by mass. How much dioxin is present in 2.5 L of this water? Assume a density of 1.00 g/mL.
