Textbook Question
Name each aldehyde or ketone. a.


 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
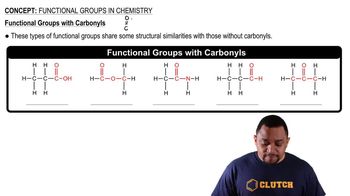

Name each aldehyde or ketone. a.
Name each aldehyde or ketone. b.
Name each aldehyde or ketone. c.
Draw the structure of each aldehyde or ketone. a. hexanal
Draw the structure of each aldehyde or ketone.
b. 2-pentanone
Draw the structure of each aldehyde or ketone. c. 2-methylbutanal