Indicate the concentration of each ion present in the solution formed by mixing: (a) 42.0 mL of 0.170 M NaOH with 37.6 mL of 0.400 M NaOH.
Ch.4 - Reactions in Aqueous Solution

Brown14th EditionChemistry: The Central ScienceISBN: 9780134414232Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 4, Problem 73a
(a) You have a stock solution of 14.8 M NH3. How many milliliters of this solution should you dilute to make 1000.0 mL of 0.250 M NH3?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the type of problem: This is a dilution problem where you need to find the volume of a concentrated solution required to make a diluted solution.
Use the dilution equation: \( C_1V_1 = C_2V_2 \), where \( C_1 \) and \( V_1 \) are the concentration and volume of the stock solution, and \( C_2 \) and \( V_2 \) are the concentration and volume of the diluted solution.
Substitute the known values into the equation: \( C_1 = 14.8 \text{ M} \), \( C_2 = 0.250 \text{ M} \), and \( V_2 = 1000.0 \text{ mL} \).
Rearrange the equation to solve for \( V_1 \): \( V_1 = \frac{C_2V_2}{C_1} \).
Calculate \( V_1 \) using the rearranged equation to find the volume of the stock solution needed.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
1mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Molarity (M)
Molarity is a measure of concentration defined as the number of moles of solute per liter of solution. It is expressed in moles per liter (mol/L) and is crucial for understanding how much solute is present in a given volume of solution. In this question, the molarity of both the stock solution and the desired diluted solution is essential for calculating the required volume of the stock solution.
Recommended video:
Guided course
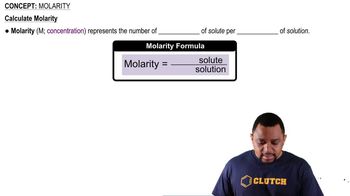
Molarity Concept
Dilution Equation
The dilution equation, often represented as M1V1 = M2V2, relates the molarity and volume of the concentrated solution (M1 and V1) to the molarity and volume of the diluted solution (M2 and V2). This equation allows us to determine how much of the concentrated solution is needed to achieve a specific concentration in a larger volume. Understanding this equation is key to solving the problem presented.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Dilution Equation
Volume Conversion
Volume conversion is the process of changing units of volume, such as from liters to milliliters. Since the question requires the final volume in milliliters, it is important to be comfortable with converting between these units. Recognizing that 1 liter equals 1000 milliliters is essential for accurately calculating the volume of the stock solution needed for dilution.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Common Conversion Factors
Related Practice
Textbook Question
2
views
Textbook Question
Indicate the concentration of each ion present in the solution formed by mixing: (b) 44.0 mL of 0.100 M Na2SO4 with 25.0 mL of 0.150 M KCl
1
views
Textbook Question
Indicate the concentration of each ion present in the solution formed by mixing: (c) 3.60 g KCl in 75.0 mL of 0.250 M CaCl2 solution. Assume that the volumes are additive.
1
views
Textbook Question
(b) If you take a 10.0-mL portion of the stock solution and dilute it to a total volume of 0.500 L, what will be the concentration of the final solution?
Textbook Question
(a) How many milliliters of a stock solution of 6.0 M HNO3 would you have to use to prepare 110 mL of 0.500 M HNO3?
Textbook Question
(b) If you dilute 10.0 mL of the stock solution to a final volume of 0.250 L, what will be the concentration of the diluted solution?
