When a 5.10-g sample of solid sodium hydroxide dissolves in 100.0 g of water in a coffee-cup calorimeter (Figure 5.18), the temperature rises from 20.5 to 33.2 °C. a. Calculate the quantity of heat (in kJ) released in the reaction.

A 2.200-g sample of quinone (C6H4O2) is burned in a bomb calorimeter whose total heat capacity is 7.854 kJ/°C. The temperature of the calorimeter increases from 23.44 to 30.57 °C. (a) What is the heat of combustion per gram of quinone?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
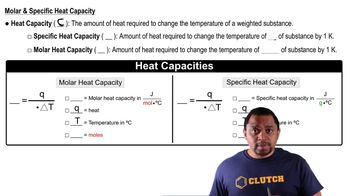
Heat Capacity
Calorimetry

Heat of Combustion
When a 5.10-g sample of solid sodium hydroxide dissolves in 100.0 g of water in a coffee-cup calorimeter (Figure 5.18), the temperature rises from 20.5 to 33.2 °C. b. Using your result from part (a), calculate ΔH (in kJ/mol NaOH) for the solution process. Assume that the specific heat of the solution is the same as that of pure water.
(b) Is this process endothermic or exothermic?
A 2.200-g sample of quinone (C6H4O2) is burned in a bomb calorimeter whose total heat capacity is 7.854 kJ/°C. The temperature of the calorimeter increases from 23.44 to 30.57 °C. b. What is the heat of combustion per mole of quinone?
A 1.800-g sample of phenol (C6H5OH) was burned in a bomb calorimeter whose total heat capacity is 11.66 kJ/°C. The temperature of the calorimeter plus contents increased from 21.36 to 26.37 °C. a. Write a balanced chemical equation for the bomb calorimeter reaction.
A 1.800-g sample of phenol (C6H5OH) was burned in a bomb calorimeter whose total heat capacity is 11.66 kJ/°C. The temperature of the calorimeter plus contents increased from 21.36 to 26.37 °C. b. What is the heat of combustion per gram of phenol?
