Textbook Question
What products are obtained in the electrolysis of a molten mixture of KI and KBr?

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


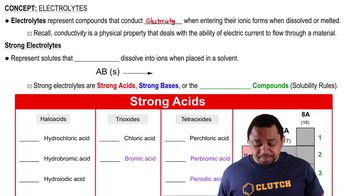
What products are obtained in the electrolysis of a molten mixture of KI and KBr?
Write equations for the half-reactions that occur at the anode and cathode for the electrolysis of each aqueous solution. a. NaBr(aq) b. PbI2(aq) c. Na2SO4(aq)
Write equations for the half-reactions that occur at the anode and cathode for the electrolysis of each aqueous solution. a. Ni(NO3)2(aq)
Make a sketch of an electrolysis cell that electroplates copper onto other metal surfaces. Label the anode and the cathode and indicate the reactions that occur at each.