You are presented with a white solid and told that due to careless labeling it is not clear if the substance is barium chloride, lead chloride, or zinc chloride. When you transfer the solid to a beaker and add water, the solid dissolves to give a clear solution. Next an Na2SO41aq2 solution is added and a white precipitate forms. What is the identity of the unknown white solid?

What kind of reaction is this? N2(g)+3H2(g)⟶2NH3(g)
a. an acid–base reaction
b. a metathesis reaction
c. a redox reaction
d. a precipitation reaction
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Types of Chemical Reactions
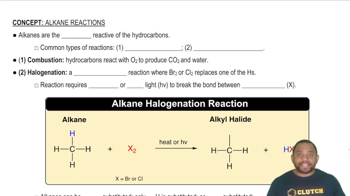
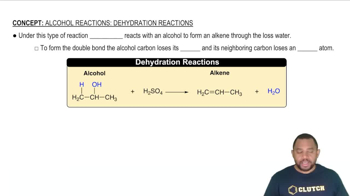
Synthesis Reaction
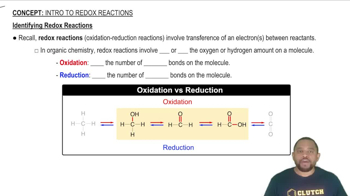
Redox Reactions
Which of the following ions will always be a spectator ion in a precipitation reaction? (a) Cl- (b) NO3- (c) NH4+ (d) S2- (e) SO42-
Which of these statements is true?
a. If a compound is oxidized, it is gaining electrons.
b. If a base is neutralized, it is gaining protons.
c. Elements that are metals cannot be oxidized.
d. If hydrogen gas is generated in a reaction, it must be an acid–base reaction.
An aqueous solution contains 1.2 mM of total ions. (a) If the solution is NaCl(aq), what is the concentration of chloride ion?
An aqueous solution contains 1.2 mM of total ions. (b) If the solution is FeCl3(aq), what is the concentration of chloride ion?
In a titration experiment, 50.0 mL of 0.075 M acetic acid, CH3COOH, is titrated with the 0.250 M KOH(aq) that is in the burette. The drawing shows the level of the KOH in the burette before the titration begins. What will be the burette reading at the equivalence point?
