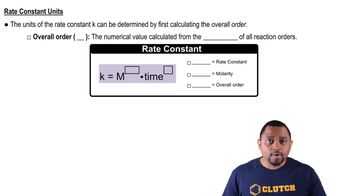
Textbook Question
For the reaction A2 + 2B ∆ 2 AB, the rate of the for- ward reaction is 18 M/s and the rate of the reverse reaction is 12 M/s. The reaction is not at equilibrium. Will the reaction pro-ceed in the forward or reverse direction to attain equilibrium?