Textbook Question
Complete each hydrogenation reaction. b.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
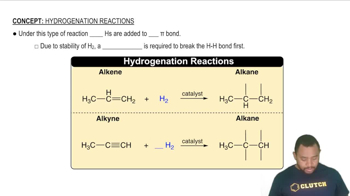
Complete each hydrogenation reaction. b.
Complete each hydrogenation reaction. a.
Complete each hydrogenation reaction. b.
Complete each hydrogenation reaction. c.
Complete each hydrogenation reaction. c.
Name each monosubstituted benzene. b.