Stars do not all have the same temperature. The color of light emitted by stars is characteristic of the light emitted by hot objects. Telescopic photos of three stars are shown below: (i) the Sun, which is classified as a yellow star, (ii) Rigel, in the constellation Orion, which is classified as a blue-white star, and (iii) Betelgeuse, also in Orion, which is classified as a red star. (a) Place these three stars in order of increasing temperature. (i) sun (ii) Rigel (iii) Betelguese

Consider the three electronic transitions in a hydrogen atom shown here, labeled A, B, and C. (a) Three electromagnetic waves, all drawn on the same scale, are also shown. Each corresponds to one of the transitions. Which electromagnetic wave (i), (ii), or (iii), is associated with electronic transition C?

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Electronic Transitions
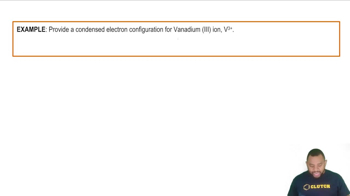
Energy Levels and Quantum Numbers
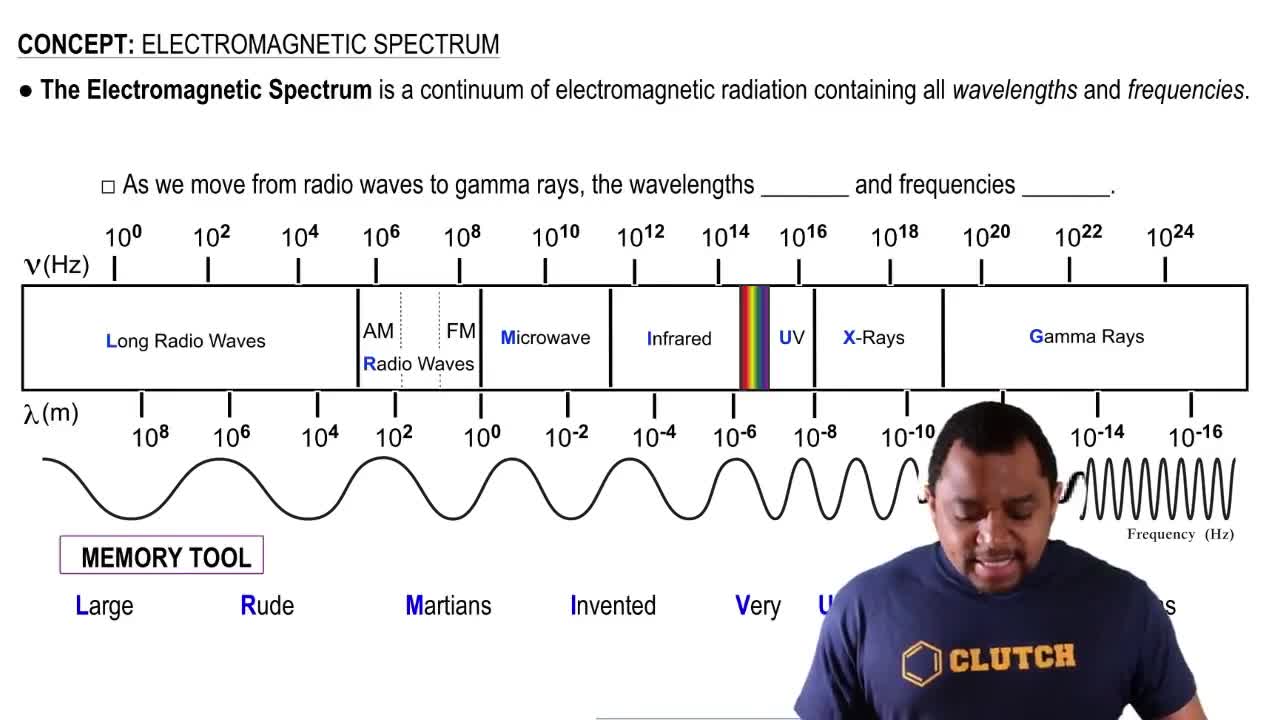
Electromagnetic Spectrum
The familiar phenomenon of a rainbow results from the diffraction of sunlight through raindrops. (a) Does the wavelength of light increase or decrease as we proceed outward from the innermost band of the rainbow?
A certain quantum-mechanical system has the energy levels shown in the accompanying diagram. The energy levels are indexed by a single quantum number n that is an integer. (b) Which quantum numbers are involved in the transition that requires the least energy?
Consider the three electronic transitions in a hydrogen atom shown here, labeled A, B, and C. (b) Calculate the energy of the photon emitted for each transition.
Calculate the energy of the photon emitted for transition C.
Consider the three electronic transitions in a hydrogen atom shown here, labeled A, B, and C. (c) Calculate the wavelength of the photon emitted for each transition. Do any of these transitions lead to the emission of visible light? If so which one(s)?
Calculate the wavelength of the photon emitted for transition B.
Consider a fictitious one-dimensional system with one electron. The wave function for the electron, drawn below, is c1x2 = sin x from x = 0 to x = 2p. (b) At what value or values of x will there be the greatest probability of finding the electron?
