List the products of each amine reaction. c.

Identify each organic compound as an alkane, alkene, alkyne, aromatic hydrocarbon, alcohol, ether, aldehyde, ketone, carboxylic acid, ester, or amine, and provide a name for the compound. e.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Hydrocarbons
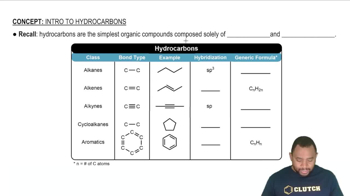
Aromatic Compounds

Nomenclature of Organic Compounds
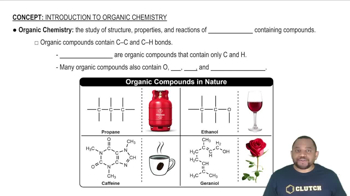
Identify each organic compound as an alkane, alkene, alkyne, aromatic hydrocarbon, alcohol, ether, aldehyde, ketone, carboxylic acid, ester, or amine, and provide a name for the compound. a.
Identify each organic compound as an alkane, alkene, alkyne, aromatic hydrocarbon, alcohol, ether, aldehyde, ketone, carboxylic acid, ester, or amine, and provide a name for the compound. c.
Identify each organic compound as an alkane, alkene, alkyne, aromatic hydrocarbon, alcohol, ether, aldehyde, ketone, carboxylic acid, ester, or amine, and provide a name for the compound. a.
Identify each organic compound as an alkane, alkene, alkyne,
aromatic hydrocarbon, alcohol, ether, aldehyde, ketone, carboxylic acid, ester, or amine, and provide a name for the compound.
c.
Identify each organic compound as an alkane, alkene, alkyne, aromatic hydrocarbon, alcohol, ether, aldehyde, ketone, carboxylic acid, ester, or amine, and provide a name for the compound. d.
