Textbook Question
Use the following solubility data to calculate a value of Ksp for each compound. (a) SrF2: 1.03 x 10-3 M (b) CuI: 1.05 x 10-6 M

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

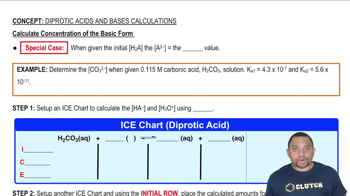

Use the following solubility data to calculate a value of Ksp for each compound. (a) SrF2: 1.03 x 10-3 M (b) CuI: 1.05 x 10-6 M
Use the following solubility data to calculate a value of Ksp for each compound. (c) MgC2O4: 0.094 g/L (d) Zn(CN)2; 4.95 x 10-4 g/L