Multiple Choice
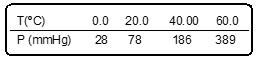
The vapor pressure of dichloromethane at 260 K is 71 torr. What is the vapor pressure at 310 K, given that ΔHvap = 31.4 kJ/mol?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
 0:59m
0:59mMaster Clausius-Clapeyron Equation with a bite sized video explanation from Jules
Start learning
