In their study of X-ray diffraction, William and Lawrence Bragg determined that the relationship among the wavelength of the radiation 1l2, the angle at which the radiation is diffracted 1u2, and the distance between planes of atoms in the crystal that cause the diffraction (d) is given by nl = 2d sin u. X rays from a copper X-ray tube that have a wavelength of 1.54 Å are diffracted at an angle of 14.22 degrees by crystalline silicon. Using the Bragg equation, calculate the distance between the planes of atoms responsible for diffraction in this crystal, assuming n = 1 (first-order diffraction).

(a) The density of diamond is 3.5 g/cm3, and that of graphite is 2.3 g/cm3. Based on the structure of buckminsterfullerene, what would you expect its density to be relative to these other forms of carbon?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
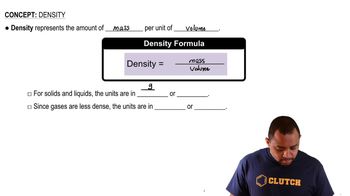
Density
Allotropes of Carbon
Molecular Structure and Density Relationship

Germanium has the same structure as silicon, but the unit cell size is different because Ge and Si atoms are not the same size. If you were to repeat the experiment described in the previous problem but replace the Si crystal with a Ge crystal, would you expect the X rays to be diffracted at a larger or smaller angle u?
(b) X-ray diffraction studies of buckminsterfullerene show that it has a face-centered cubic lattice of C60 molecules. The length of an edge of the unit cell is 14.2 Å. Calculate the density of buckminsterfullerene.
The karat scale used to describe gold alloys is based on mass percentages. (a) If an alloy is formed that is 50 mol% silver and 50 mol% gold, what is the karat number of the alloy? Use Figure 12.18 to estimate the color of this alloy.
