Textbook Question
What hybridization do you expect for the atom that is underlined in each of the following species? (a) IO2- (b) NH4+ (c) SCN- (d) BrCl3

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

What hybridization do you expect for the atom that is underlined in each of the following species? (a) IO2- (b) NH4+ (c) SCN- (d) BrCl3
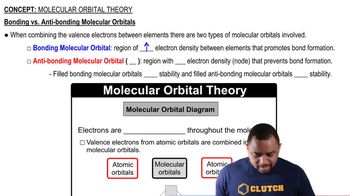
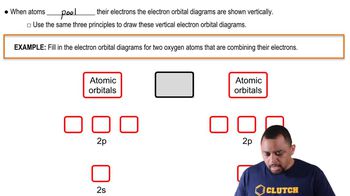
Consider the H2+ ion. (a) Sketch the molecular orbitals of the ion and draw its energy-level diagram.
Consider the H2+ ion. (b) How many electrons are there in the H2+ ion?
Consider the H2+ ion. (c) Write the electron configuration of the ion in terms of its MOs. (d) What is the bond order in H2+?