In the Brønsted–Lowry concept of acids and bases, acid– base reactions are viewed as proton-transfer reactions. The stronger the acid, the weaker is its conjugate base. If we were to think of redox reactions in a similar way, what particle would be analogous to the proton? Would strong oxidizing agents be analogous to strong acids or strong bases? [Sections 20.1 and 20.2]
Ch.20 - Electrochemistry

Brown14th EditionChemistry: The Central ScienceISBN: 9780134414232Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 20, Problem 3a
The diagram that follows represents a molecular view of a process occurring at an electrode in a voltaic cell.

(a) Does the process represent oxidation or reduction?

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the process occurring at the electrode by observing the movement of particles in the diagram.
Note that the particles are moving away from the electrode, indicating a loss of particles from the electrode surface.
Understand that in a voltaic cell, oxidation occurs at the anode where there is a loss of electrons, and reduction occurs at the cathode where there is a gain of electrons.
Recognize that the loss of particles from the electrode suggests that the electrode is losing electrons, which is characteristic of oxidation.
Conclude that the process represented in the diagram is oxidation, as the electrode is losing particles (electrons).

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
53sWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Oxidation and Reduction
Oxidation and reduction are chemical processes that involve the transfer of electrons between species. Oxidation refers to the loss of electrons, while reduction involves the gain of electrons. In a voltaic cell, these processes occur at the electrodes, where oxidation typically happens at the anode and reduction at the cathode. Understanding which process is occurring is crucial for analyzing electrochemical reactions.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Oxidation and Reduction Reactions
Voltaic Cell
A voltaic cell, also known as a galvanic cell, is a device that converts chemical energy into electrical energy through spontaneous redox reactions. It consists of two electrodes (anode and cathode) immersed in an electrolyte solution. The flow of electrons from the anode to the cathode generates an electric current, making it essential to understand the roles of each electrode in the overall reaction.
Recommended video:
Guided course

The Electrolytic Cell
Electron Flow
In electrochemical cells, the flow of electrons is a fundamental concept that dictates the direction of current and the type of reaction occurring. Electrons flow from the anode, where oxidation occurs, to the cathode, where reduction takes place. This movement is crucial for the functioning of the voltaic cell and is visually represented in diagrams showing electron transfer during the redox process.
Recommended video:
Guided course
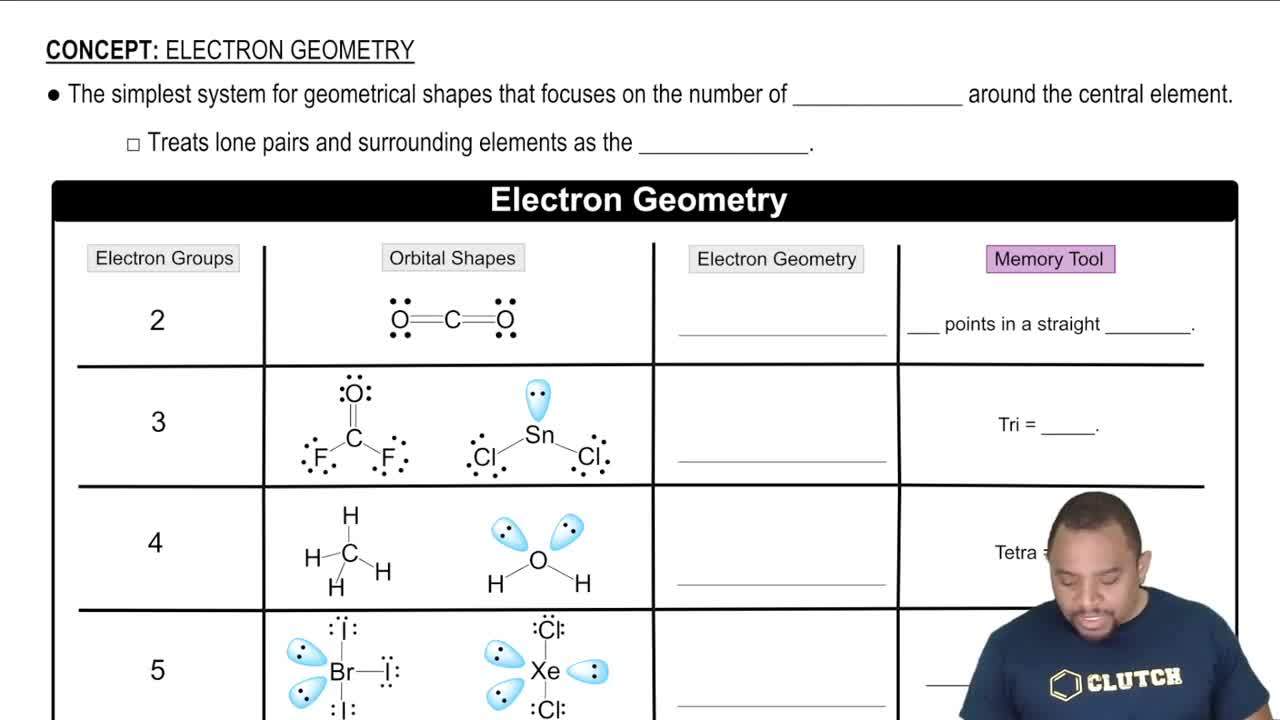
Electron Geometry
Related Practice
Textbook Question
3
views
Textbook Question
The diagram that follows represents a molecular view of a process occurring at an electrode in a voltaic cell.
(b) Is the electrode the anode or cathode?
1
views
Textbook Question
The diagram that follows represents a molecular view of a process occurring at an electrode in a voltaic cell.
(c) Why are the atoms in the electrode represented by larger spheres than those in the solution? [Section 20.3]
Textbook Question
Assume that you want to construct a voltaic cell that uses the following half-reactions: A2+1aq2 + 2 e- ¡ A1s2 Ered ° = -0.10 V B2+1aq2 + 2 e- ¡ B1s2 E°red = -1.10 V You begin with the incomplete cell pictured here in which the electrodes are immersed in water.
(a) What additions must you make to the cell for it to generate a standard emf?
1
views
