Textbook Question
Draw the structure of each aldehyde or ketone. d. 4-heptanone

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Draw the structure of each aldehyde or ketone. d. 4-heptanone
Determine the product of the addition reaction.
Determine the product of the addition reaction.
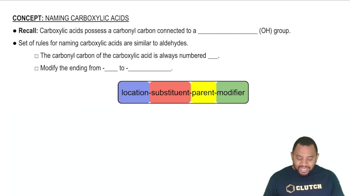
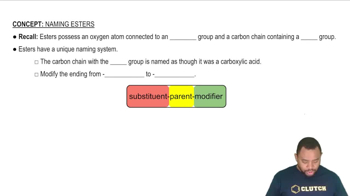
Name each carboxylic acid or ester.
Name each carboxylic acid or ester.
Name each carboxylic acid or ester.