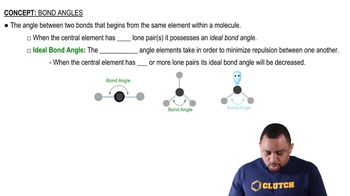
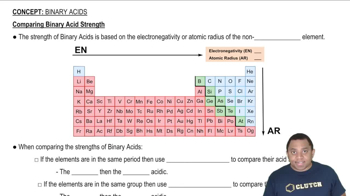
Elemental Properties
The properties of elements, such as electronegativity, atomic size, and the ability to hybridize, play a crucial role in determining the strength of bonds they can form. For instance, elements with higher electronegativity can stabilize π bonds more effectively, while those with suitable p-orbitals can participate in π bonding more readily.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance