Textbook Question
(a) True or false: 'solubility' and 'solubility-product constant' are the same number for a given compound.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
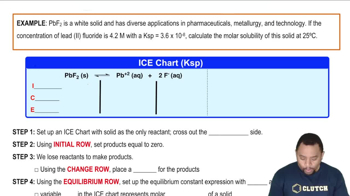


(a) True or false: 'solubility' and 'solubility-product constant' are the same number for a given compound.
(b) Write the expression for the solubility-product constant for each of the following ionic compounds: MnCO3, Hg(OH)2, and Cu3(PO4)3.
(b) It is found that 1.1 × 10-2 g SrF2 dissolves per 100 mL of aqueous solution at 25°C. Calculate the solubility product for SrF2.
(b) If 0.0490 g of AgIO3 dissolves per liter of solution, calculate the solubility-product constant.