Using Lewis symbols and Lewis structures, diagram the formation of PF3 from P and F atoms, showing valence-shell electrons. (e) Does PF3 obey the octet rule?
Ch.8 - Basic Concepts of Chemical Bonding

Brown14th EditionChemistry: The Central ScienceISBN: 9780134414232Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 8, Problem 36a
(a) Construct a Lewis structure for hydrogen peroxide, H2O2, in which each atom achieves an octet of electrons.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the total number of valence electrons in the molecule. Hydrogen (H) has 1 valence electron and Oxygen (O) has 6 valence electrons. Therefore, for H2O2, calculate the total valence electrons as: 2(1) + 2(6) = 14 valence electrons.
Arrange the atoms with the least electronegative atom in the center. In H2O2, the structure is linear with the two oxygen atoms in the center: H-O-O-H.
Connect the atoms with single bonds initially. Each single bond represents 2 electrons. So, connect H-O, O-O, and O-H with single bonds, using 8 electrons in total (4 bonds x 2 electrons each).
Distribute the remaining valence electrons to satisfy the octet rule for each atom. Start by placing the remaining electrons around the oxygen atoms to complete their octets. Each oxygen should have 8 electrons around it, including those in bonds.
Check that all atoms have achieved a full valence shell. Hydrogen atoms should have 2 electrons (1 bond), and each oxygen should have 8 electrons (including shared electrons in bonds). Adjust if necessary to ensure all atoms satisfy their respective electron requirements.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
1mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Lewis Structures
Lewis structures are diagrams that represent the bonding between atoms in a molecule and the lone pairs of electrons that may exist. They use dots to represent valence electrons and lines to represent bonds between atoms. Constructing a Lewis structure involves determining the total number of valence electrons, arranging atoms, and ensuring that each atom achieves a stable electron configuration, typically an octet for main group elements.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Lewis Dot Structures: Ions
Octet Rule
The octet rule is a chemical principle that states that atoms tend to bond in such a way that they each have eight electrons in their valence shell, achieving a stable electronic configuration similar to that of noble gases. This rule is particularly applicable to main group elements and guides the formation of covalent bonds, where atoms share electrons to fulfill this requirement.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Octet Rule
Valence Electrons
Valence electrons are the electrons in the outermost shell of an atom that are involved in forming bonds with other atoms. The number of valence electrons determines an element's chemical properties and its ability to bond with other elements. In the case of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), understanding the valence electrons of hydrogen and oxygen is crucial for constructing its Lewis structure and ensuring that all atoms achieve an octet where applicable.
Recommended video:
Guided course
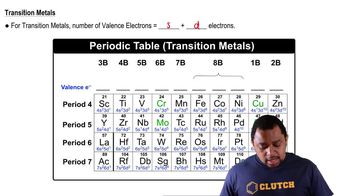
Transition Metals Valence Electrons
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
(b) How many bonding electrons are in the structure?
Textbook Question
(c) Would you expect the O—O bond in O2 to be shorter or longer than the O—O bond in compounds that contain an O—O single bond? Explain.
Textbook Question
(c) Do you expect the O—O bond in H2O2 to be longer or shorter than the O—O bond in O2? Explain.
Textbook Question
Which of the following statements about electronegativity is false? (a) Electronegativity is the ability of an atom in a molecule to attract electron density toward itself. (b) Electronegativity is the same thing as electron affinity. (c) The numerical values for electronegativity have no units. (d) Fluorine is the most electronegative element. (e) Cesium is the least electronegative element.
