Periodic Table Trends
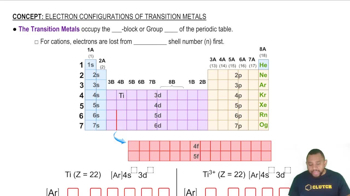
The periodic table organizes elements based on their atomic number and electron configuration, revealing trends in properties such as electronegativity, ionization energy, and electron affinity. By understanding these trends, one can predict the behavior of elements like copper and determine the number of electrons in specific orbitals, such as the 3d subshell.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance