Textbook Question
Determine the number of protons and the number of electrons in each ion. c. Ga3+

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
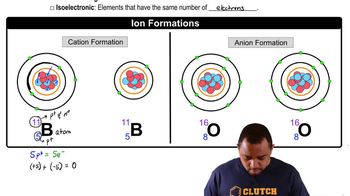

Determine the number of protons and the number of electrons in each ion. c. Ga3+
Determine the number of protons and the number of electrons in each ion. d. Sr2+
Predict the charge of the ion formed by each element. a. Sr
Fill in the blanks to complete the table.
Symbol Ion Formed Number of Electrons in Ion Number of Protons in Ion
Cl ______ ______ 17
Te ______ 54 ______
Br Br– ______ ______
______ Sr2+ ______ 38
Write the symbol for each element and classify it as a metal, nonmetal, or metalloid. a. bromine b. potassium c. lead d. silicon e. silver
Determine whether or not each element is a main-group element. a. tellurium b. potassium c. vanadium d. manganese