Consider the collection of nonmetallic elements O, P, Te, I, and B. (b) Which two would form the longest single bond?

The substance chlorine monoxide, ClO(g), is important in atmospheric processes that lead to depletion of the ozone layer. The ClO molecule has an experimental dipole moment of 1.24 D, and the Cl—O bond length is 160 pm. (c) Using formal charges as a guide, propose the dominant Lewis structure for the molecule. (g), is important in atmospheric processes that lead to depletion of the ozone layer. The ClO molecule has an experimental dipole moment of 1.24 D, and the Cl—O bond length is 160 pm. (d) The anion ClO exists. What is the formal charge on the Cl for the best Lewis structure for ClO-?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Lewis Structures

Formal Charge

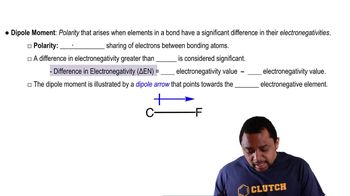
Dipole Moment
Consider the collection of nonmetallic elements: B, As, O, and I. (d) Which element would likely to participate in two covalent bonds?
The substance chlorine monoxide, ClO(g), is important in atmospheric processes that lead to depletion of the ozone layer. The ClO molecule has an experimental dipole moment of 1.24 D, and the Cl—O bond length is 160 pm. (b) Based on the electronegativities of the elements, which atom would you expect to have a partial negative charge in the ClO molecule?
(a) Using the electronegativities of Br and Cl, estimate the partial charges on the atoms in the Br¬Cl molecule.
(b) Using these partial charges and the atomic radii given in Figure 7.8, estimate the dipole moment of the molecule.
(c) The measured dipole moment of BrCl is 0.57 D. If you assume the bond length in BrCl is the sum of the atomic radii, what are the partial charges on the atoms in BrCl using the experimental dipole moment?
