Textbook Question
Draw a picture that shows all three 2p orbitals on one atom and all three 2p orbitals on another atom. (b) How many p bonds can the two sets of 2p orbitals make with each other?

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
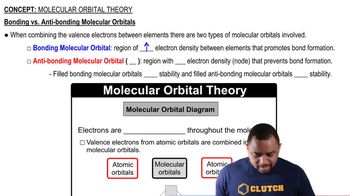

Draw a picture that shows all three 2p orbitals on one atom and all three 2p orbitals on another atom. (b) How many p bonds can the two sets of 2p orbitals make with each other?
Draw a picture that shows all three 2p orbitals on one atom and all three 2p orbitals on another atom. (c) How many antibonding orbitals, and of what type can be made from the two sets of 2p orbitals?
Indicate whether each statement is true or false. (a) p orbitals can only make σ or σ* molecular orbitals.
Indicate whether each statement is true or false. (c) Molecules containing electrons that occupy antibonding orbitals must be unstable.
Indicate whether each statement is true or false. (d) Electrons cannot occupy a nonbonding orbital.