Table of contents
- 0. Functions(0)
- Introduction to Functions(0)
- Piecewise Functions(0)
- Properties of Functions(0)
- Common Functions(0)
- Transformations(0)
- Combining Functions(0)
- Exponent rules(0)
- Exponential Functions(0)
- Logarithmic Functions(0)
- Properties of Logarithms(0)
- Exponential & Logarithmic Equations(0)
- Introduction to Trigonometric Functions(0)
- Graphs of Trigonometric Functions(0)
- Trigonometric Identities(0)
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions(0)
- 1. Limits and Continuity(0)
- 2. Intro to Derivatives(0)
- 3. Techniques of Differentiation(0)
- 4. Applications of Derivatives(0)
- 5. Graphical Applications of Derivatives(0)
- 6. Derivatives of Inverse, Exponential, & Logarithmic Functions(0)
- 7. Antiderivatives & Indefinite Integrals(0)
- 8. Definite Integrals(0)
- 9. Graphical Applications of Integrals(0)
- 10. Physics Applications of Integrals (0)
- 11. Integrals of Inverse, Exponential, & Logarithmic Functions(0)
- 12. Techniques of Integration(0)
- 13. Intro to Differential Equations(0)
- 14. Sequences & Series(0)
- 15. Power Series(0)
- 16. Parametric Equations & Polar Coordinates(0)
5. Graphical Applications of Derivatives
Applied Optimization
5. Graphical Applications of Derivatives
Applied Optimization: Videos & Practice Problems
31 of 0
Problem 31Multiple Choice
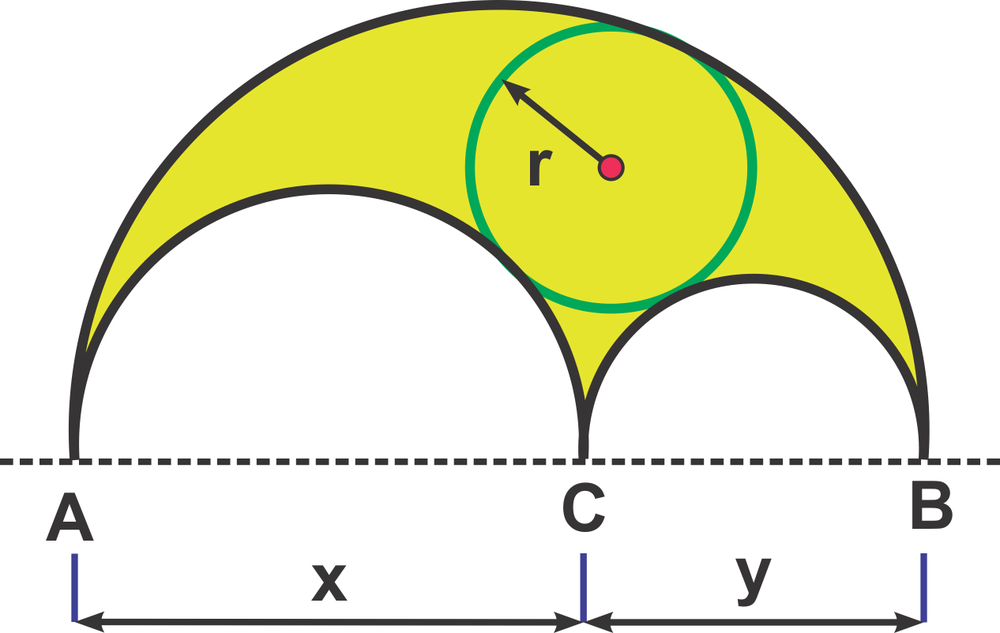
The shaded region in the figure is called an arbelos, formed by three mutually tangent semicircles. The incircle is the largest circle that can fit inside the arbelos, and it is tangent to all three semicircles. If the largest semicircle has a diameter of , what should be the diameter of one of the smaller semicircles to maximize the radius of the incircle ? Note that the radius of the incircle can be expressed in terms of the diameters of the two smaller semicircles as follows:
0 Comments
