Table of contents
- 0. Functions(0)
- Introduction to Functions(0)
- Piecewise Functions(0)
- Properties of Functions(0)
- Common Functions(0)
- Transformations(0)
- Combining Functions(0)
- Exponent rules(0)
- Exponential Functions(0)
- Logarithmic Functions(0)
- Properties of Logarithms(0)
- Exponential & Logarithmic Equations(0)
- Introduction to Trigonometric Functions(0)
- Graphs of Trigonometric Functions(0)
- Trigonometric Identities(0)
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions(0)
- 1. Limits and Continuity(0)
- 2. Intro to Derivatives(0)
- 3. Techniques of Differentiation(0)
- 4. Applications of Derivatives(0)
- 5. Graphical Applications of Derivatives(0)
- 6. Derivatives of Inverse, Exponential, & Logarithmic Functions(0)
- 7. Antiderivatives & Indefinite Integrals(0)
- 8. Definite Integrals(0)
- 9. Graphical Applications of Integrals(0)
- 10. Physics Applications of Integrals (0)
- 11. Integrals of Inverse, Exponential, & Logarithmic Functions(0)
- 12. Techniques of Integration(0)
- 13. Intro to Differential Equations(0)
- 14. Sequences & Series(0)
- 15. Power Series(0)
- 16. Parametric Equations & Polar Coordinates(0)
1. Limits and Continuity
Introduction to Limits
1. Limits and Continuity
Introduction to Limits: Videos & Practice Problems
154 of 0
Problem 154Multiple Choice
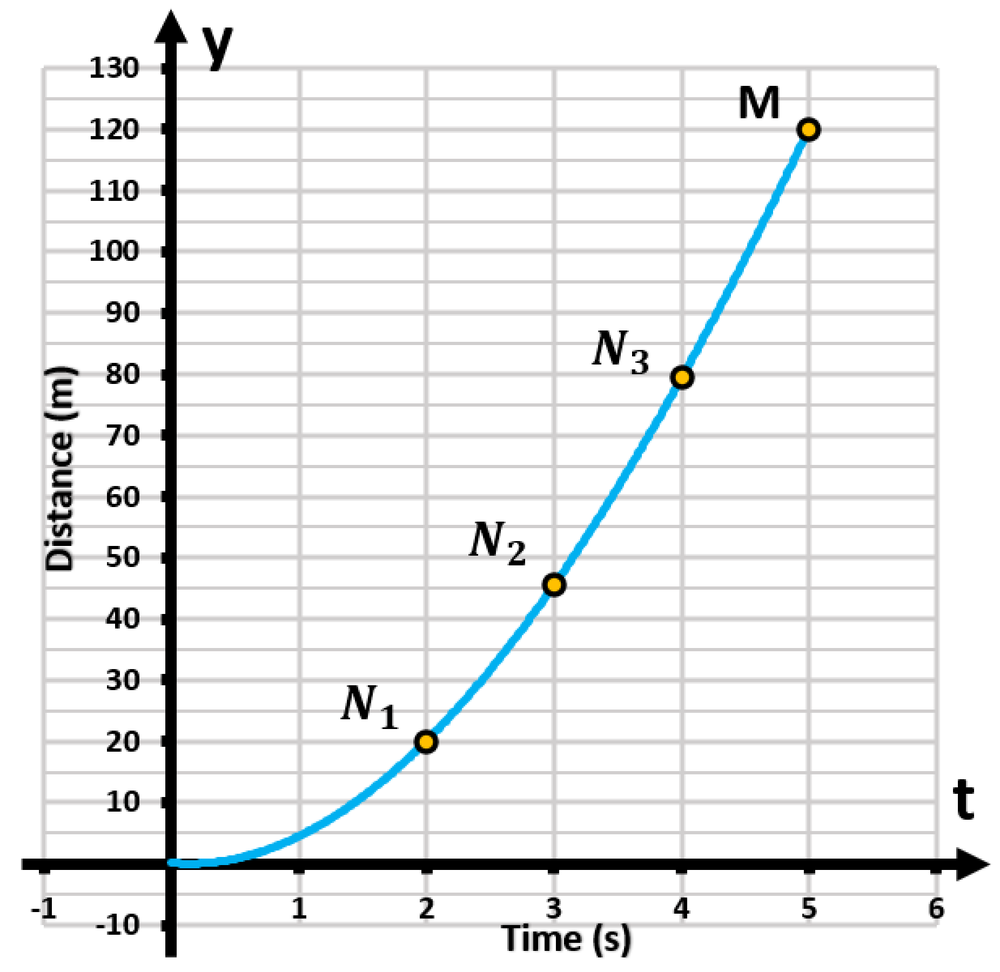
During a physics experiment, a ball is dropped from rest at a height of above the ground. The figure shows the plot of distance fallen versus time for the ball as it descends due to Earth's gravity. Estimate the slopes of the secant lines , , and . Approximately how fast was the ball moving when it reached the ground? Round your answers to one decimal place.
0 Comments
