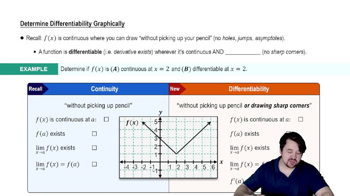
Use a graph of f to estimate or to show that the limit does not exist. Evaluate f(x) near to support your conjecture.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:


 6:47m
6:47mMaster Finding Limits Numerically and Graphically with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick
Start learning