Choose the pair of terms that correctly completes this sentence: Catabolism is to anabolism as ____________ is to ____________.
a. exergonic; spontaneous
b. exergonic; endergonic
c. free energy; entropy
d. work; energy

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
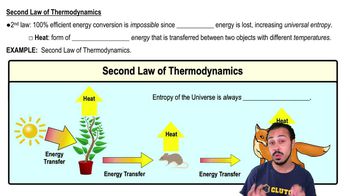
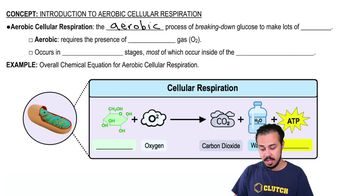

Choose the pair of terms that correctly completes this sentence: Catabolism is to anabolism as ____________ is to ____________.
a. exergonic; spontaneous
b. exergonic; endergonic
c. free energy; entropy
d. work; energy
Which of the following metabolic processes can occur without a net influx of energy from some other process?
a. ADP + Ⓟi → ATP + H2O
b. C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O
c. 6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2
d. Aminoacids →Protein
If an enzyme in solution is saturated with substrate, the most effective way to obtain a faster yield of products is to
a. Add more of the enzyme.
b. Heat the solution to 90°C.
c. Add more substrate.
d. Add a noncompetitive inhibitor.
Some bacteria are metabolically active in hot springs because
a. They are able to maintain a lower internal temperature.
b. High temperatures make catalysis unnecessary.
c. Their enzymes have high optimal temperatures.
d. Their enzymes are completely insensitive to temperature.